Why Circular Textile?
Over the last 15 years, clothing production has doubled, but the effective use of clothing has dropped by 40%. In a pattern where manufacturers are selling more, but consumers are using less, our planet's resources are continually being depleted. The linear economic approach of "take-make-use-dispose" leads to excessive consumption, emissions, pollution, and worsens the impact of climate change. The global textile supply chain faces various risks, including extreme climate events and disruptions, while the worldwide commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 introduces new complexities. If the textile industry maintains its business-as-usual operations, it will consistently deplete resources. Neglecting a significant hole in the water tank resulted in a leakage of over a hundred billion dollars' worth every year.
Why Taiwan Needs Circular Textile?
The Taiwanese textile industry has accumulated experience in utilizing recycled fibers, arising from Taiwan's inherent limitations of lacking abundant natural resources. Taiwan’s textile industry relies heavily on raw material manufacturing, exposing it to risks associated with fluctuations in raw material prices and market dynamics. On one side, brands exert pressure to minimize waste and emissions, while on the other, raw material prices continue to rise. While the industry may gain its expertise in utilizing recycled materials, it can no longer depend extensively on raw materials, exposing itself to the heightened risks of fluctuations in both material availability and market dynamics.
Circular Textile considers the entire textile lifecycle, aiming to extend the lifespan of textiles, reduce reliance on raw resources, and actively respond to global commitments for net-zero emissions. This transformation is vital for Taiwan's textile industry, minimizing environmental impact and enhancing operational resilience through circular strategies and reduced dependence on raw materials. Circular Textile elevates the industry to a combination of quality products and services, embracing a circular mindset throughout the textile lifecycle. Leveraging Taiwan's global leadership in functional fabrics, the industry can design a closed-loop system and foster the transition from “Made in Taiwan” to “Circular in Taiwan.”
Handbook Chapters:
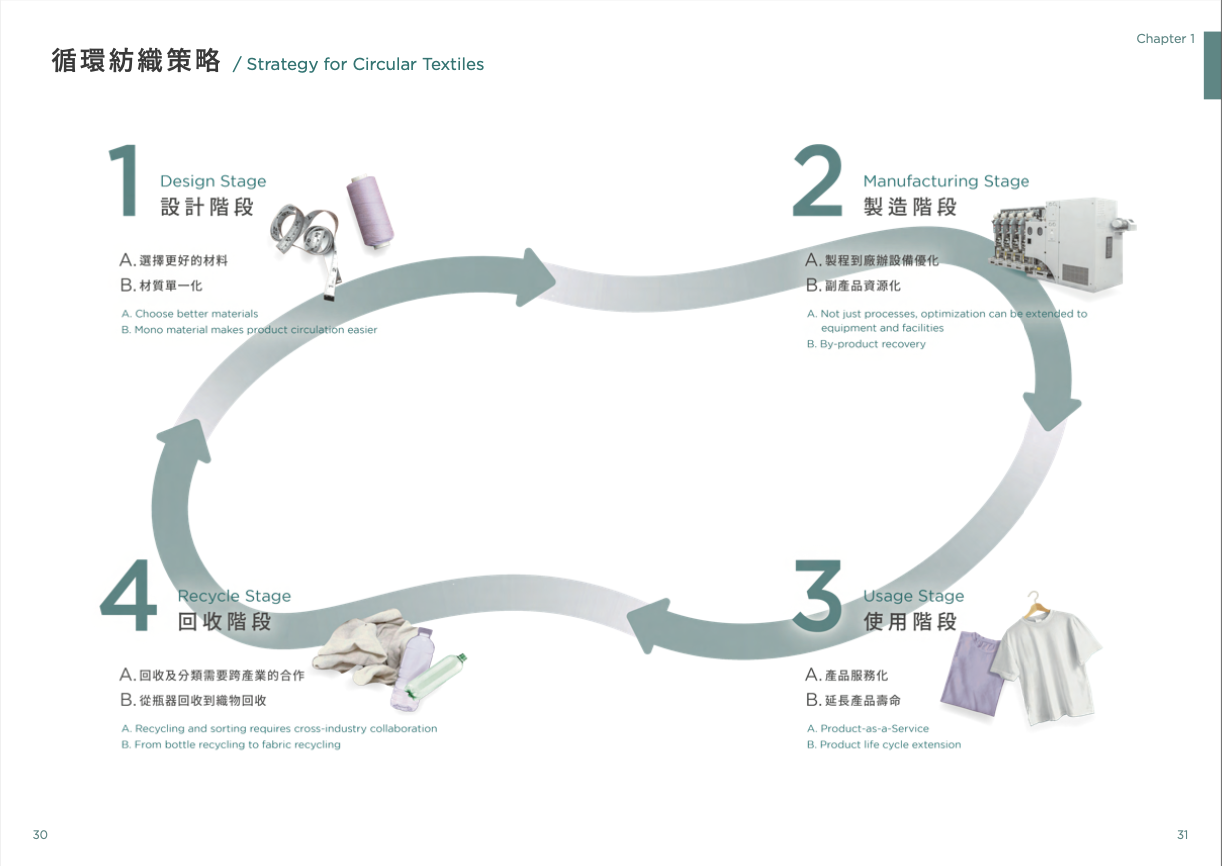
- Chapter 1: Presents the current global material flow in the textile industry and proposes a closed-loop circular strategy for the entire lifecycle of textiles.
- Chapter 2: Features eight cases in Taiwan, illustrating initial achievements of Taiwanese textile businesses in the circular economy.
- Chapter 3: Summarizes the advantages of Taiwan's textile industry and explores the unique role the industry can play in the global context.